Present Indefinite Tense|Definition, rules, Structure, Examples
When the verb of a sentence shows an action, without mentioning its completeness or incompleteness, then this sentence is said to be of the “Simple Present Tene or Present Indefinite Tense”. It means that the Present Indefinite Tense simply mentions an action that would be going on in the present time. It has nothing to do with the completeness or incompleteness of an action.
Helping Verbs of Present Indefinite Tense
Present Indefinite Tense has the following helping verbs that are used with specific pronouns and a specific number of nouns.
Both these helping verbs “do/ does”, only appear in negative and interrogative sentences of Simple Present Tense or Present Indefinite Tense.
“Do” as a Helping Verb in the Present Indefinite Tense
“Do” acts as a helping verb in Negative and Interrogative Sentences of Present Indefinite Tense with the following pronouns and plural number of nouns.
- You
- I
- They
- We

“Does” as Helping Verb in the Present Indefinite Tense
“Does” is used as a helping verb in Negative and Interrogative Sentences of Present Indefinite Tense with the following pronouns and a singular number of nouns.
- He
- She
- It

Sentence Structure of Present Indefinite Tense
Present Indefinite Tense has the following sentence structure of Assertive, Negative, Interrogative, and Negative-Interrogative Sentences:
Assertive Sentence Structure of Simple Present Tense or Present Indefinite Tense
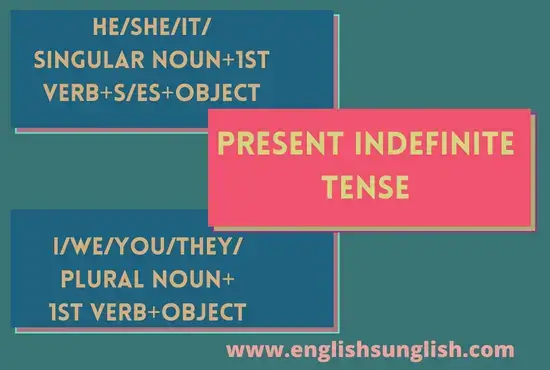
Assertive Sentences of the Present Indefinite Tense do not take any helping verb “do/does“, instead the verb takes “s/ es” with the following pronouns and a singular number of nouns.
- He
- she
- It
Assertive Sentences of the Present Indefinite Tense have the following Sentence Structure Formula with singular pronouns (except I) and nouns:
Subject + Verb + e/es + Object + Remaining Words
While with the plural pronouns, nouns, and also the pronoun “I”, the Assertive Sentence of Present Indefinite Tense has the following Sentence Structure Formula.
Subject + Verb + Object + Remaining Words

Examples of Assertive Sentences of Present Indefinite Tense
Following are examples of Assertive Sentences of Present Indefinite Tense:
Examples of Assertive Sentences with singular pronouns and nouns
With singular nouns and pronouns, Assertive Sentences of Simple Tense take s/es with 1st Verb.
- He goes to school daily.
- He offers prayers five times a day.
- John cleans his teeth.
- She sews clothes.
- Ali buys books.
- Saad goes to the office daily.
- He does his work.
- He draws a map of England.
- The washerman washes the clothes.
- Naseema weeps.
- The peon rings the bell regularly.
- She plucks flowers.
- He reads various kinds of magazines.
- She prefers milk to tea.
- He goes to school every day.
- David is a good football player.
- He represents the Stars Club.
- He always offers his best services to his relatives.
- He is a zealous player and plays with a passion for his country.
- He reads good books.
- Marry washes the clothes clean.
- The goat gives milk.
- She always speaks the truth.
- Sun gives us life.
- Water boils at 100 degrees Celsius and freezes at 0 degrees Celsius.
Examples of Assertive Sentences with plural pronouns and nouns
Verbs appear in their original form and never take “s/es” while using plural pronouns and nouns.
- I solve the question.
- Parrots talk.
- Jackals howl in the evening.
- The shoemakers make shoes.
- You learn the lesson.
- You deal in sugar.
- I wear new clothes.
- Girls sing songs.
- Hardworking students get prizes.
- We go outside for a walk.
- They get up early in the morning.
- You eat an apple.
- They play Cricket.
- Azhar and Ijaz talk with each other.
- There are stars in the sky.
- The children catch the ball.
- We read.
- They run very fast.
- They come to school on time.
- You take a bath daily.
- I get up early in the morning.
- We do our work ourselves.
- We go to the market daily.
- I write essays on different topics.
- They love to play hockey.
- We come for shopping in this mall.
- We watch thrill movies in that Cinema.
- You always shop from this shop.
- I sing different kinds of songs.
- I love to travel around the World.
- We always play cricket on that field.
- I know how to protest against injustice.
- I love my family very much.
- I like him for his honesty.
Negative Sentence Structure of Present Indefinite Tense
Negative Sentences of the Present Indefinite Tense use “do/does” with “not” to indicate the negativity of sentences.
Negative Sentences have the following Structure with singular pronouns and nouns.
Subject + does not + 1st form of Verb + Object + Remaining Words
Negative Sentences have the following Structure with plural pronouns and nouns.
Subject + do not + 1st form of Verb + Object + Remaining Words

Examples of Negative Sentences of Present Indefinite Tense
Following are examples of Negative Sentences of Simple Present Tense or Present Indefinite Tense:
Examples of Negative Sentences with Singular Pronouns and Nouns
Negative Sentences of Present Indefinite Tense uses “does not” as a helping verb with singular pronouns and nouns to show the negativity of the sentences. In Negative Sentences of singular pronouns and nouns, the verb does not take “s/es” with them, instead, it appears in its original form. For example:
- He does not write a letter.
- She does not write a letter.
- He does not go to the office.
- He does not take exercise regularly.
- She does not always speak the truth.
- The goat does not eat meat.
- He does not hate anyone.
- The girl does not call her mother.
- Your brother does not look after the cow.
- He does not repent of sin.
- He does not listen to me.
- A wise man does not make such a mistake.
- The sun does not revolve around the earth.
- The moon does not appear in the evening these days.
- Wood does not sink in water.
- A piece of iron does not float in water.
- John does not save anything.
Examples of Negative Sentences with Plural Pronouns and Nouns
Negative Sentences of Present Indefinite Tense use “do not” as a helping verb with plural pronouns and nouns to show the negativity of the sentences. For example:
- I do not write a letter.
- We do not write a letter.
- You do not write a letter.
- They do not write a letter.
- They do not go home at noon.
- We do not live in Lahore.
- They do not get up early in the morning.
- They do not do their work.
- You do not go for a walk in the evening.
- I do not wish to meet him.
- We do not like boxing.
- Horses do not run in the desert.
- We do not boast of our ability.
- We do not run this factory.
- Good boys do not abuse anyone.
- Good friends do not cheat.
- You do not confess your fault.
- Uninteresting books do not sell like hotcakes.
- The stars do not shine in the day.
- I do not recognize this stranger.
- We do not know you.
- All the boys do not make mischief.
- We do not tease anyone for anything.
Interrogative Sentence Structure of Present Indefinite Tense
Interrogative Sentences of Present indefinite Tense take “do/does” at the start of Sentences and Question Mark (?) at the end to show the question. However, with the Words of Questions (where, when, why, how, what), “do/does” appear after the Words of Questions.
Interrogative Sentence Structure with the Words of Questions (where, why, when, what, how).
Word of Question + do/does + 1st form of Verb + Object + Remaining Words + Question Mark(?)
Interrogative Sentence Structure with singular nouns and pronouns.
Does + Subject + 1st form of Verb + Object + Remaining Words + Question Mark(?)
Interrogative Sentence Structure with plural nouns and pronouns.
Do + Subject + 1st form of Verb + Object + Remaining Words + Question Mark(?)

Examples of Interrogative Sentences of Present Indefinite Tense
Following are examples of Interrogative Sentences of Present Indefinite Tense:
Examples of Interrogative Sentences with Words of Questions
“Do/does” appears after the Words of Questions in the Interrogative Sentences and the Question Mark (?) at the end. For example:
- Where do children play hide and seek?
- When does the postman come into this street?
- Why do you object to his stay over here?
- Why does he spend more than his income?
- How long does she stay with her maternal uncle?
- Where does the army encamp?
- Why do these students waste time?
- When does the cock crow?
- Why does the cloth merchant give short measures?
- Why do you insist on buying only a bicycle?
- When do the birds chirp?
- Why do the people sing and dance on Urs?
- What kind of dreams do you see?
- Why do you not show me translation exercises?
- When does it snow on mountains?
Examples of Interrogative Sentences with Singular Pronouns and Nouns
Interrogative Sentences with singular pronouns and nouns take “does”, at the start of the Sentence to pose a question and Question Mark (?) at the end. For example:
- Does the cloud thunder loudly?
- Does it hail in summer?
- Does he feel ashamed of what he did?
- Does Harry wander till late at night?
- Does your daughter respect the elders?
- Does he demand a reasonable price for the fox?
- Does the rich man burn the candle at both ends?
- Does this girl sleep late at night?
- Does he know his mistake?
- Does this class take interest in its work?
- Does it rain only in summer in Pakistan/India?
- Does he read a book?
- Does the dog bark at night?
- Does she take tea daily?
- Does Sunrise at 6’O clock?
- Does the farmer plow the field?
- Does the shopkeeper sell cloth?
- Does he get up late in the morning?
- Does he fly kite?
- Does he go to the office on time?
Examples of Interrogative Sentences with Plural Pronouns and Nouns
Interrogative Sentences with plural pronouns and nouns take “do”, at the start of the Sentence to pose a question and Question Mark (?) at the end. For example:
- Do you prefer fruit to sweets?
- Do people deem time important?
- Do all the students collect postage stamps?
- Do they not care for anybody?
- Do I read a book?
- Do we read books?
- Do you eat food?
- Do they wash clothes?
- Do you love your country?
- Do birds live in their nests?
- Do we go for walk daily?
- Do fish swim in water?
- Do your watch the show right time?
- Do teachers call the roll?
- Do horses eat grass?
- Do boys make a noise?
- Do we worship God?
- Do birds fly in the air?
- Do you offer prayer?
Negative Interrogative Sentence Structure of Present Indefinite Tense
Negative Interrogative Sentences of Present indefinite Tense take “do/does” at the start of the Sentences and Question Mark (?) at the end to show the question. However, with the Words of Questions (where, when, why, how, what), “do/does” appear after the Words of Questions. “Not” comes after the “Subject” of the Sentence to show the negativity of the Negative-Interrogative Sentence.
Negative Interrogative Sentence Structure with the Words of Questions (where, why, when, what, how).
Word of Question + do/does + not + 1st form of Verb + Object + Remaining Words + Question Mark(?)
Negative Interrogative Sentence Structure with singular nouns and pronouns.
Does + Subject + not + 1st form of Verb + Object + Remaining Words + Question Mark(?)
Negative Interrogative Sentence Structure with plural nouns and pronouns.
Do + Subject + not + 1st form of Verb + Object + Remaining Words + Question Mark(?)

Examples of Negative-Interrogative Sentences of Present Indefinite Tense
Following are some examples of Negative-Interrogative Sentences.
Examples of Negative-Interrogative Sentences of Present Indefinite Tense with Words of Questions
“Do/does” appears after the Words of Questions in the Negative-Interrogative Sentences and the Question Mark (?) at the end. For example:
- Where do children not play hide and seek?
- When does the postman not come into this street?
- Why do you not object to his stay over here?
- Why does he not spend more than his income?
- How long does she not stay with her maternal uncle?
- Where does the army not encamp?
- Why do these students not waste time?
- When does the cock not crow?
- Why does the cloth merchant not give short measures?
- Why do you not insist on buying only a bicycle?
- When do the birds not chirp?
- Why do people not sing and dance?
- What kind of dreams do you not see?
- Why do you not show me translation exercises?
- When does it not snow on mountains?
Examples of Interrogative Sentences of Present Indefinite Tense with Singular Pronouns and Nouns
Interrogative Sentences with singular pronouns and nouns take “does”, at the start of the Sentence to pose a question and Question Mark (?) at the end. For example:
- Does the cloud not thunder?
- Does it not hail in summer?
- Does he not feel ashamed of what he did?
- Does Harry not wander till late at night?
- Does your daughter not respect the elders?
- Does he not demand a reasonable price for the fox?
- Does the rich man not burn the candle at both ends?
- Does this girl not sleep late at night?
- Does he not know his mistake?
- Does this class not take interest in its work?
- Does it not rain only in summer in Pakistan/India?
- Does he not read a book?
- Does the dog not bark at night?
- Does she not take tea daily?
- Does Sun not rises at 6’O clock?
- Does the farmer not plow the field?
- Does the shopkeeper not sell cloth?
- Does he not get up late in the morning?
- Does he not fly kite?
- Does he not go to the office at the time?
Examples of Negative-Interrogative Sentences of Present Indefinite Tense with Plural Pronouns and Nouns
Negative-Interrogative Sentences with plural pronouns and nouns take “do”, at the start of the Sentence to pose a question and Question Mark (?) at the end. For example:
- Do you not prefer fruit to sweets?
- Do people not deem time important?
- Do all the students not collect postage stamps?
- Do they not care for anybody?
- Do I not read a book?
- Do we not read books?
- Do you not eat food?
- Do they not wash clothes?
- Do you not love your country?
- Do birds not live in their nests?
- Do we not go for walk daily?
- Do fish not swim in water?
- Do you not watch the show right time?
- Do teachers not call the roll?
- Do horses not eat grass?
- Do boys not make a noise?
- Do we not worship God?
- Do birds not fly in the air?
- Do you not offer prayer?
- They should think not twice, but thrice, before ignoring such advice.
Passive Voice of Present Indefinite Tense
Active Voice of Present Indefinite can be converted into Passive Voice. Passive Voice of Present Indefinite Tense uses “is/are/am” as a helping verb under certain rules as cited in the following blog post: