English Grammar Tenses| definition, types, use, examples

The word “tense” has come from the Latin word “Tempus”, which means “time”. It means that tenses are used to show the time of an action/ state. Tenses play a vital role in all languages because they tell about the period during which something has happened. In English, there are three main types of tenses as follows:
Each of these three types of tenses has further 4 other types, depending on the state of an action/event as follows:
- Indefinite
- Continuous
- Perfect
- Perfect Continuous
These 4 sub-divided tenses show actions in Present, Past, and Future tenses. Thus, in the English language, 3 basic types of tenses can be further subdivided into 12 other types as follow.
Present Tense Types
All the actions or states that have a present-period presence, are called to be in the Present Tense. Present-time actions can be divided into the following 4 types, depending on the phase of action.
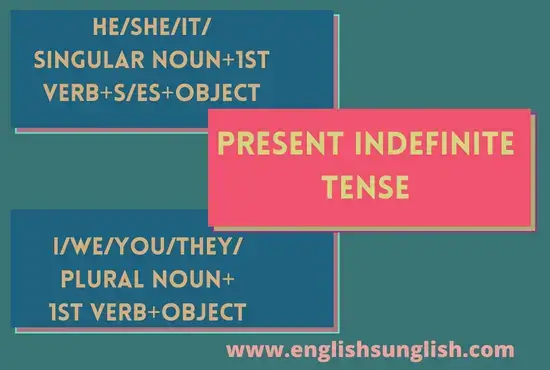
- Simple Present Indefinite Tense
- Present Continuous Tense
- Present Perfect Tense
- Present Perfect Continuous Tense
A Verb that is used to indicate the Present Time Actions, is said to be in the Present Tense. For example:
- I write this letter to tell him about my health.
- I am writing this letter to tell him about my health.
- I have already written a letter to tell him about my health.
- I have been writing several letters to tell him about my health.
Past Tense Types
Like Present Tense, Past Tense also has all the actions under the following 4 domains.
- Simple Past Indefinite Tense
- Past Continuous Tense
- Past Perfect Tense
- Past Perfect Continuous Tense
A Verb that is used to refer to Past Time Actions, is said to be in the Past Tense. For example:
- I wrote this letter to tell him about my health.
- I was writing this letter to tell him about my health.
- I had written a letter to tell him about my health.
- I had been writing several letters to tell him about my health.
Future Tense Types
Just like Present and Past tenses, Future Tense also has the following 4 types.
- Simple Future Indefinite Tense
- Future Continuous Tense
- Future Perfect Tense
- Future Perfect Continuous Tense
A Verb that is used to indicate Future Time Actions, is said to be in the Future Tense. For example:
- I shall write a letter to tell him about my health.
- I shall be writing a letter to tell him about my health.
- I shall have written a letter to tell him about my health.
- I shall have been writing several letters to tell him about my health.
Abnormal behavior of Present, Past, and Future Tenses
Present, Past, and Future tenses, sometimes, act differently. For example:
Past Tense as Present Tense
In certain circumstances, Past Tense is used to indicate the happening of something in the Present Time. In such circumstances, one part of the sentence shows some hope or wish for past time. For example:
- I wish I knew the answer.
- I wish I were a millionaire.
- I wish I cooked it well.
- I wish I passed this exam.
- I wish I knew how to sing.
Present Tense as Future Tense
Under certain conditions, the Present Tense is used to indicate the happening of something in the Future. In such conditions, the Present Tense may have some command or order for the future event. It means that the Present Tense can be used in the Future Tense sense for arrangements and plans. For example:
- Let’s wait till he comes.
- The train leaves at 7 pm.
- The course starts in January.
- I go to school next Friday.
- The plane is expected to land in one hour.